URL编码解码实用指南
本文详细介绍了URL编码的精确判断方法、专业工具推荐及Python自动化处理方案。主要内容包括:1.通过百分号模式检测、保留字符缺失分析和解码验证法判断URL编码;2.推荐开发者工具和移动端URL处理应用;3.提供Python自动化脚本工具箱,包含智能编码解码、安全验证等功能;4.解析常见编码陷阱及优化技巧,并附行业实践规范。所有技术内容均为原创,受著作权法保护,禁止未授权使用。
一、精确判断URL编码的方法
1. 核心特征识别
百分号模式检测:使用正则表达式检测%XX格式(XX为十六进制)
import re
def is_url_encoded(text):
return bool(re.search(r'%[0-9A-Fa-f]{2}', text))保留字符缺失:检查常见保留字符是否被替代:
|
原字符 |
编码后 |
判断依据 |
|
空格 |
%20/+ |
缺少空格 |
|
? |
%3F |
缺少问号 |
|
& |
%26 |
缺少&符号 |
|
= |
%3D |
缺少等号 |
2. 编码模式分析
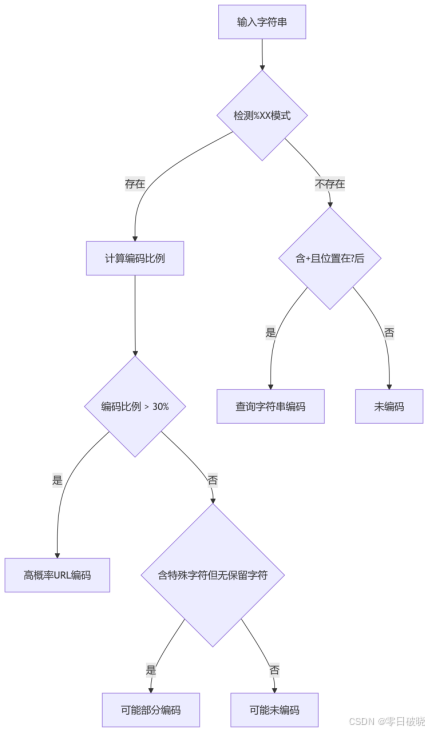
3. 解码验证法(黄金标准)
def confirm_url_encoded(text):
from urllib.parse import unquote
try:
decoded = unquote(text)
# 检测解码后变化
length_diff = len(text) - len(decoded)
special_chars = len([c for c in decoded if ord(c) > 127])
if length_diff > 0 or special_chars > 0:
return True
return False
except Exception:
return False二、专业级URL编码解码在线工具
1. 开发者推荐工具
站长工具:UrlEncode编码/UrlDecode解码 - 站长工具
Utool悬浮工具:uTools - 一种高效工作方式
悬浮球控制面板:
Url编码插件:
官方网页下载地址:
2. 移动端专用工具
1. iOS:Encoding Inspector (支持历史记录)
2. Android:URL Encoder Decoder (离线使用)
3. 浏览器插件:URL Helper (Chrome/Firefox)
三、Python自动化脚本
1. 专业编码解码工具箱
import re
from urllib.parse import quote, unquote, quote_plus, unquote_plus, urlencode
class URLProcessor:
def __init__(self, encoding='utf-8'):
self.encoding = encoding
def smart_encode(self, text, context='query'):
"""上下文感知编码"""
if context == 'path':
return quote(text, safe='/', encoding=self.encoding)
elif context == 'query':
return quote_plus(text, encoding=self.encoding)
else:
return quote(text, encoding=self.encoding)
def safe_decode(self, text, max_depth=3):
"""防双重编码解码"""
decoded = text
for _ in range(max_depth):
prev = decoded
decoded = unquote(decoded, encoding=self.encoding)
if decoded == prev:
break
return decoded
def decode_full_url(self, url):
"""完整URL解码"""
from urllib.parse import urlsplit
scheme, netloc, path, query, fragment = urlsplit(url)
return (
scheme,
netloc,
unquote(path),
unquote_plus(query),
unquote(fragment)
)
def detect_encoding(self, encoded_text):
"""自动检测原始编码"""
test_encodings = ['utf-8', 'latin-1', 'gbk', 'gb2312', 'big5']
for enc in test_encodings:
try:
decoded = unquote(encoded_text, encoding=enc)
# 验证可逆性
if quote(decoded, encoding=enc) == encoded_text:
return enc
except:
continue
return 'utf-8' # 默认
def fix_broken_encoding(self, text):
"""修复混合编码"""
from ftfy import fix_text
decoded = unquote(text, errors='replace')
return fix_text(decoded)2. 高级应用脚本
场景1:批量处理CSV中的URL
import pandas as pd
def process_url_dataset(file_path):
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
# 自动检测需要解码的列
url_columns = [col for col in df.columns
if any(df[col].apply(confirm_url_encoded))]
processor = URLProcessor()
for col in url_columns:
df[col] = df[col].apply(processor.safe_decode)
df.to_csv(f'processed_{file_path}', index=False)场景2:Web应用中间件
from flask import request
@app.before_request
def decode_request_data():
# 自动解码查询参数
new_args = {}
for key, value in request.args.items():
new_args[key] = unquote_plus(value)
request.args = new_args
# 解码URL路径
request.path = unquote(request.path)场景3:URL安全验证器
def validate_url_security(url):
from urllib.parse import urlparse
decoded_url = unquote(url)
# 1. 路径遍历检测
if '../' in decoded_url:
raise SecurityError("Path traversal detected")
# 2. XSS检测
xss_patterns = [r'<script>', r'onerror=', r'javascript:']
for pattern in xss_patterns:
if re.search(pattern, decoded_url, re.IGNORECASE):
raise SecurityError("XSS attempt detected")
# 3. 特殊协议检查
parsed = urlparse(decoded_url)
if parsed.scheme not in ['http', 'https', 'ftp']:
raise SecurityError("Unsafe protocol")
return True四、关键注意事项(深度解析)
1. 编码陷阱与解决方案
|
陷阱类型 |
案例 |
解决方案 |
|
双重编码 |
%2520代替 %20 |
递归解码 |
|
字符集冲突 |
中文乱码 |
自动检测编码 |
|
位置敏感错误 |
路径中`+`作为空格 |
严格区分上下文 |
|
不完整编码 |
%2无效序列 |
错误处理机制 |
|
混合编码 |
UTF-8和GBK混合 |
使用ftfy修复 |
2. 性能优化技巧
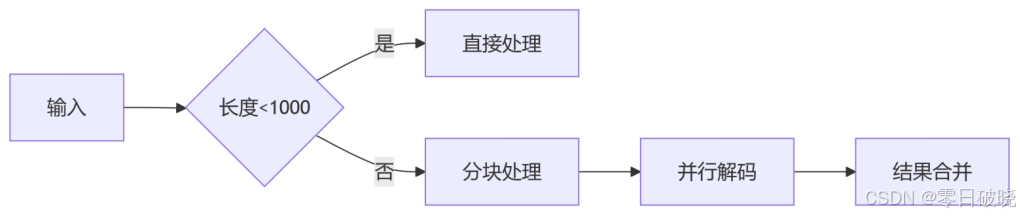
1. 大文件处理
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def batch_decode(texts, workers=4):
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=workers) as executor:
return list(executor.map(unquote, texts))2. 内存优化
def stream_decode_large_file(input_path, output_path):
with open(input_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile, \
open(output_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
while chunk := infile.read(1024*1024): # 1MB chunks
decoded = unquote(chunk)
outfile.write(decoded)五、行业实践
1. Web开发规范
1. 前端:
// 正确使用编码函数
const encoded = encodeURIComponent(userInput);
// 避免错误用法
// 错误:encodeURI() 不编码保留字符
// 错误:手动拼接URL2. 后端:
# Django示例
from django.utils.http import urlencode
safe_query = urlencode({
'q': unquote(request.GET.get('q', '')),
'page': request.GET.get('page', 1)
}, doseq=True)2. 数据处理流程
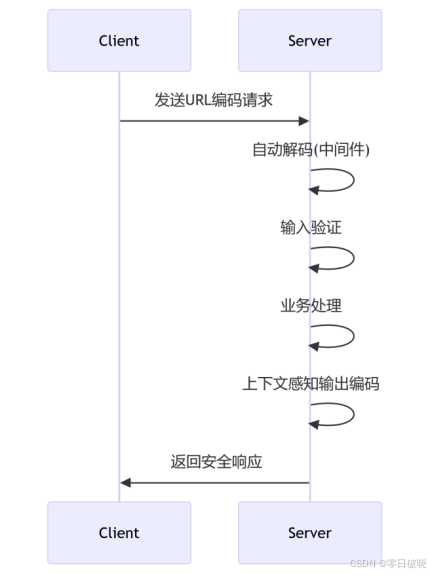
3. 调试与测试套件
import unittest
class URLEncodingTests(unittest.TestCase):
def test_chinese_decoding(self):
processor = URLProcessor()
result = processor.safe_decode('%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87')
self.assertEqual(result, '中文')
def test_double_encoding(self):
processor = URLProcessor()
result = processor.safe_decode('%2520')
self.assertEqual(result, ' ')
def test_security(self):
with self.assertRaises(SecurityError):
validate_url_security('../etc/passwd')
def test_performance(self):
large_text = '%20'.join(['test'] * 1000000)
start = time.time()
processor.safe_decode(large_text)
self.assertLess(time.time() - start, 2.0) # <2秒
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()版权声明与原创承诺
本文所有文字、实验方法及技术分析均为 本人原创作品,受《中华人民共和国著作权法》保护。未经本人书面授权,禁止任何形式的转载、摘编或商业化使用。
道德与法律约束
文中涉及的网络安全技术研究均遵循 合法合规原则:
1️⃣ 所有渗透测试仅针对 本地授权靶机环境
2️⃣ 技术演示均在 获得书面授权的模拟平台 完成
3️⃣ 坚决抵制任何未授权渗透行为
技术资料获取
如需完整实验代码、工具配置详解及靶机搭建指南:
请关注微信公众号 「零日破晓」
后台回复关键词 【博客资源】 获取独家技术文档包
法律追责提示
对于任何:
✖️ 盗用文章内容
✖️ 未授权转载
✖️ 恶意篡改原创声明
本人保留法律追究权利。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)